Prostatitis is characterized as inflammation of the prostate tissue, resulting from the development of congestion in it.
In the modern world, it is the most common urological disease among men of all ages. According to statistics, after 30 years of age, prostatitis covers 30% of the male population, after 40-40%, after 50-50% and thereafter in ascending order.
However, taking into account the peculiarities of the diagnosis and the possibility of latent disease evolution, the real numbers are much higher.
reasons for development
Currently, the causes of the development of prostatitis are divided into two major groups:
- Infectious - (sexually transmitted infections (penetration in the prostate tissues of the causative agent - microbes, viruses, bacteria, fungi, etc. ): also the presence of chronic infection foci (chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, renal pathology), operations on Organs pelvic organs and etc. ).
- Non-infectious (stagnant) (decreased immunity, hypothermia, decreased physical activity, sedentary lifestyle, prolonged sexual abstinence and vice versa, excessive sexual activity, alcohol abuse, etc. ).
The development of prostatitis is facilitated by lesions, reduced blood and lymphatic circulation in Organs pelvic organs, hormonal disturbances (absolute or relative androgen deficiency).
Thus, it is noteworthy that the isolated entry of the pathogen into the organ's tissues is not always and may not necessarily be the cause of the development of the disease. The most frequently identified pathogen is Escherichia coli (86%), followed by Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. With regard to streptococci, staphylococci, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, researchers' opinions on their importance in the development of the disease are divergent. It is extremely rare for specific pathogens (treponema pallidum, Koch's bacillus, etc. ) to become the cause of prostatitis.
Classification
Currently, the international classification of prostatitis is adopted, which is the most complete and covers all types of inflammation:
- Category I. Acute prostatitis;
- Category II. Chronic bacterial prostatitis;
- Category III. Chronic Nonbacterial Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome - a disease in which no infection is detected that lasts longer than 3 months;
- Subcategory III A. Chronic Inflammatory Pelvic Pain Syndrome (WBCs are determined in the secret of the prostate);
- Subcategory III B. Non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome (no leukocytes in the prostate secret);
- Category IV. Asymptomatic chronic prostatitis (the leukocytes are present in the secret of the prostate, the patient has no complaints, the disease is detected by chance).
first signs
The main signs of acute prostatitis are an increase in body temperature and frequent urination, which is accompanied by cramps and low blood pressure. Also, signs of prostatitis include a burning sensation in the perineum and pain in the rectum during bowel movements. In the purulent inflammation stage, spontaneous opening of the abscess and flow of pus from the urethra or rectum is likely.
A symptom of a chronic form is burning in the urethra and perineum, discharge of pus at the end of the act of defecating or urinating, increased fatigue and irritability in the body.
Difficulty urinating with prostatitis is very dangerous and, in the absence of timely treatment, can cause acute urinary retention. Men should not ignore indirect signs of developing prostatitis, such as a complete or partial decrease in libido, accelerated ejaculation, sometimes painful, prolonged erection at night. All of these symptoms are characteristic of prostate inflammation, even at an uncomplicated and treatable stage.
Symptoms
If acute prostatitis is simply impossible not to notice, then in chronic prostatitis, many do not notice certain signs or attach special importance to them.
Let's list the main symptoms of prostatitis in men:
- Problems with urination. Due to the narrowing of the urethra, the jet may be slow, thin, or intermittent. To empty, the patient has to make an effort, which should not be normal. Sometimes urine literally needs to be squeezed out drop by drop, especially in the early stages of urination. Painful sensations often occur. Many patients have frequent urges to urinate (especially at night), this is due to irritation of the nerve endings. Even after going to the bathroom, many have the feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied, this is due to an enlarged prostate and bladder compression. In severe cases, involuntary leakage of urine or incontinence may occur.
- Painful sensations. As a rule, they are located in the perineum, pubis or testicles, in the groin or lower back. The pain can occur suddenly and go away just as quickly, it is often quite severe, but more often it has a dull or painful character.
- Sexual problems will inevitably arise. First, the libido will significantly decrease. Second, erection problems can occur. Thirdly, due to problems with ejaculation (ejaculation), the average duration of intercourse will change: it may become short due to premature ejaculation or, conversely, very long due to delayed ejaculation. Fourth, the sensations will also change as the orgasm will not be brilliant. Fifth, the semen volume will be significantly reduced (only a few drops can be released, which is not normal).
- Another characteristic symptom is problems with conception. If a man is planning a child, then with prostatitis, fertilization becomes impossible due to the infeasibility or insufficient mobility of the sperm.
- Discharge of the urethra. They are usually white in color and slimy in texture and are most common in the morning.
- In the acute course, there is an increase in body temperature (up to 38-39 °), fever, deterioration of the general condition, weakness, malaise and other similar manifestations. These prostatitis symptoms usually appear suddenly without any prerequisites.
Also, many have psychological problems associated with the symptoms listed above. A man may be insecure, his self-esteem will be greatly reduced, he will be depressed or angry and nervous. Many representatives of the stronger sex are ashamed of such delicate problems and don't find it necessary to talk about them, keeping everything to themselves. And that puts a lot of pressure on the psyche, changes behavior, and in some cases can lead to depression or nervous breakdown.
chronic prostatitis
Many men don't pay much attention to the manifestations of prostatitis in the early stages. These are mild painful sensations in the bladder area, frequent need to go to the bathroom. Violation of normal ejaculation and erection is associated with stronger sex with age and there is no rush to see a doctor. This frivolous attitude leads to the development of chronic prostatitis.
Therefore, we've listed the common symptoms of various forms of chronic prostatitis:
- Feeling of discomfort and cuts in the urethra during urination or intercourse, small serous-purulent discharge from the urethra (mainly after prolonged urinary retention).
- Discomfort and/and moderate pain in the form of "pains" and heaviness in the perineal region, appearing or worsening after drinking alcohol, physical activity, sexual intercourse. Sometimes they are of a transient paroxysmal nature.
- Decreased fertilization capacity, caused by increased secretion acidity, decreased or lack of sperm motility and their agglutination (gluing) by the heads.
- Sudden and frequent urge to urinate (sometimes up to 3 times in 1 hour) and a feeling of insufficient bladder emptying, which is explained by a violation of the nerve regulation of the prostate, its muscle fibers and bladder.
- Pain during orgasm or blurred orgasm sensations, ejaculation disorders, expressed in their prematurity or, conversely, in the excessive duration of intercourse. These phenomena are associated with an inflammatory process in the seminal tubercle area or scarring as a result of inflammation.
To diagnose the condition, you will need to see a urologist. With the help of tests, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes a course of drug treatment.
Diagnosis
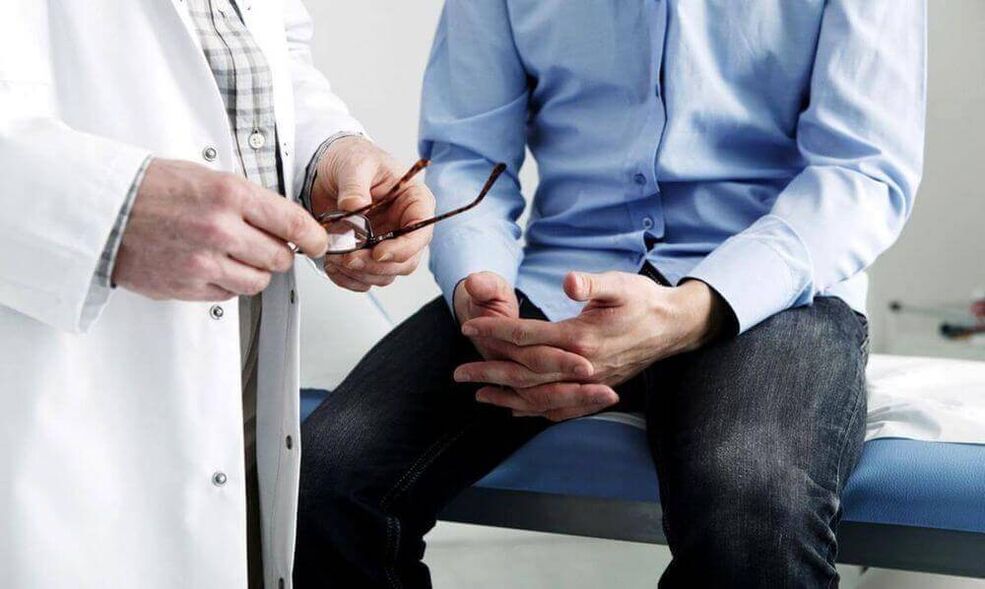
To make an accurate diagnosis, a man needs to be examined by a doctor and tested. In prostatitis, the patient feels pain on palpation in the perineal region. The internal palpation of the rectum shows the presence of swelling in the prostate region, it becomes dense to the touch. The patient complains of problems with the genitourinary system. After taking the anamnesis, the patient must undergo a detailed blood test to check for the presence of excess protein, increased white blood cell count and prostatic antigen.
To exclude infection, the patient must smear the urethra. The laboratory will inoculate the identified bacteria and test their sensitivity to certain types of antibiotics. To obtain an accurate image, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is performed. It clearly shows inflammation and enlargement of the prostate. If the gland has grown strongly, then on ultrasound you can see residual urine in the bladder.
After all tests and exams have passed, the man will have a complete diagnosis and prescribed treatment.
Medications for the treatment of prostatitis in men: a list
Complex treatment for prostatitis of various types may include different combinations of the following methods:
- immunocorrective therapy;
- antibiotic therapy;
- hormone therapy;
- various physical therapy procedures;
- prostate massage;
- lifestyle change;
- surgical intervention, etc.
Drug treatment of prostatitis includes several drugs, including antibiotics:
- alpha blockers;
- hormonal drugs;
- muscle relaxants;
- immunomodulators;
- rectal suppositories;
- antibacterial drugs.
In antibiotic treatment, preference is given to fluoroquinols and macrolides, as they can accumulate in the necessary concentration in the tissues of the prostate.
- Fluoroquinols.
- Macrolides.
- Less commonly used: penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines.
prostate massage
Prostate massage shows good results. The gland receives a complex effect. First, it becomes possible to remove from the body the inflammatory secret that has accumulated in the prostate (it is released during massage). Improving blood circulation through these manipulations allows you to deal with all types of stagnation and also contributes to good penetration of antibiotics into the gland tissue.
a set of exercises
Exercises for the prostate:
- Absolutely not a difficult exercise is used for both treatment and prevention. It consists of contracting and relaxing the muscles of the anus. These muscles are responsible for containing the flow when urinating. Try to contract and open a muscle group. This will increase blood flow to the gland area.
- Use a contrast shower to improve circulation. To do this, direct the water flow to the perineum. First 30 seconds of very hot water, then 10 seconds of cold water.
- In the absence of acute symptoms, you can massage yourself. This is done to improve blood flow. The best way to do the exercise is lying down. The point for the massage is the gap between the anus and the scrotum. Pressures should be firm but not aggressive. Time is 3-5 minutes.
Be sure to consult your doctor before exercising. Sometimes its use is categorically unacceptable.
immunocorrection
Decreased immunity negatively affects health.
This factor is one of the fundamental factors in the development of the disease and its aggravation. Long-term courses of antibiotics, which are mandatory for persistent prostatitis, also reduce the body's defenses. Therefore, it is recommended that the patient consults an immunologist to choose a strategy for performing immunocorrection.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy for chronic prostatitis aims to activate blood circulation.
For that, the patient is exposed to laser, and magnetic vibrations are used. In some cases, these procedures are replaced by hot medicinal enemas, which are regularly administered to the patient. Recommend sitz baths, mud treatment, mineral waters.
Candles
All suppositories for the treatment of prostatitis have one of the following properties: relieving pain (non-steroidal drugs), relieving spasms (based on papaverine), eliminating the inflammatory process (containing an antibiotic).
Alternative methods of treating prostatitis
Home treatment of prostatitis is performed only in uncomplicated or chronic relapse forms. Traditional methods can increase the body's resistance to infections and relieve pain.
- Pumpkin seeds have long been used by healers to treat prostatitis. They are a good and very affordable folk remedy for this condition. Because these seeds contain a lot of zinc needed by any man of any age, they quickly cure prostatitis. You only need to eat 30 seeds a day before meals. This is exactly the daily ratio of zinc to the body.
- The plant's seeds and roots are suitable. The crushed roots of the plant are boiled for 10 minutes at a rate of half a cup of raw material per 1 liter of water. All broth is drunk in equal portions instead of water. The seeds are prepared in 4 teaspoons per cup of boiling water. Insist 40 minutes in a saucepan or 15 minutes in a thermos. Consume about 3-5 times a day for a tablespoon.
- The main ingredient is hazelnut. To treat prostatitis, you need to remove the hazelnut's husk or leaves. You can prepare the two ingredients alternately, alternating between them. Be aware that the husk needs to be fermented twice as much as it is harder. Then, take a tablespoon of hazelnut leaves (or husk) and boil it in a cup of boiling water. Close the lid tightly and wait half an hour. Then strain and drink 1/4 cup 4 times a day. It's best to use new branches all the time, but you can also use the ones you've already used over and over again. Usually a week of these procedures is enough - and the prostatitis goes away.
- To treat the disease, candles are made and stored in the freezer. For the dough, take 1 teaspoon of honey, 1 egg and about 3 tablespoons of flour. The components are mixed until homogeneous, forming candles. Used in two courses in the morning and in the evening, 1 piece per 1 month with a 10-day break.
- Celandine is used with caution. The plant is poisonous, an overdose leads to severe poisoning. At the same time, the celandine medicine will clean the body of polyps, neoplasms, cysts and prevent prostate adenoma. The freshly squeezed juice is diluted with alcohol in equal parts. Drink it daily, diluting it in 50 ml of water. Start treatment with 1 drop, increasing concentration by 1 drop every day for 60 days. After 10 days the course is repeated.
Most folk remedies are used 1-3 times daily in courses of 20-30 days. Treatment with herbal home remedies lasts longer because of their moderate effect than with medicines, but it is safer for the body, especially in the presence of concomitant illnesses of the intestines and stomach. The treatment must be accompanied by gymnastics: lifting the legs, squatting. Intensive walking is recommended for 15-30 minutes daily.

Complications of Prostatitis
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, prostatitis can be complicated by the following conditions:
- the development of chronic prostatitis;
- bladder obstruction;
- the development of infertility;
- recurrent cystitis;
- urethra narrowing;
- pyelonephritis;
- prostate abscess;
- sepsis.
Some of the conditions above require urgent surgical intervention!
prevention measures
Prevention boils down to avoiding provocation factors. A healthy lifestyle, protected sex and the presence of a partner reduce the likelihood of genitourinary system infection. Overall strengthening of the body and increasing immune defenses are also preventive measures for prostatitis.